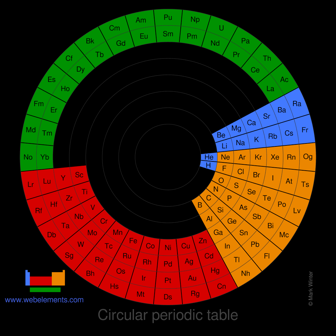
Images of circular periodic tables of the elements
The periodic table is an arrangment of the chemical elements ordered by atomic number so that chemical periodic properties of the elements (chemical periodicity) are made clear.
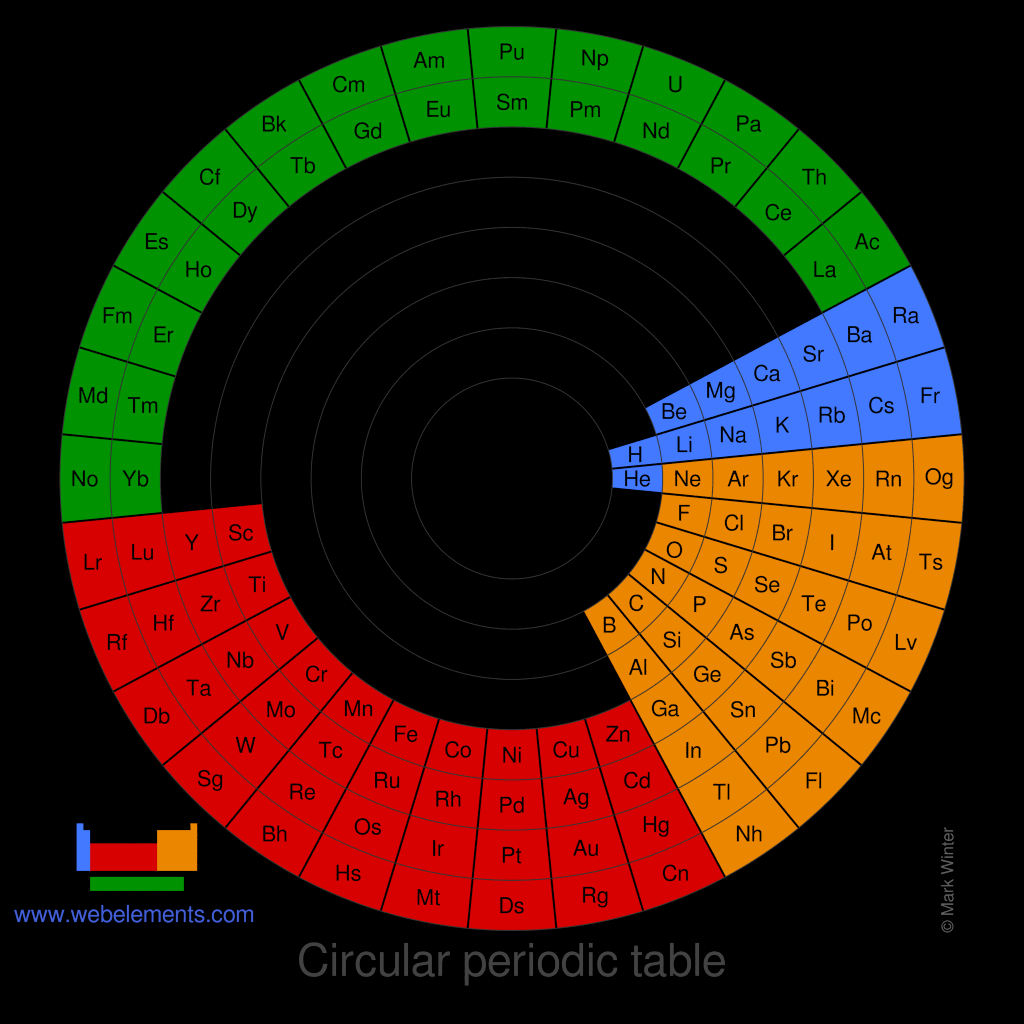
There is no one single or best structure for the periodic table. Circular forms of the periodic table do not quite demonstrate strict atomic number ordering. Perhaps spiral forms do this better.
Image of a circular periodic table of the elements
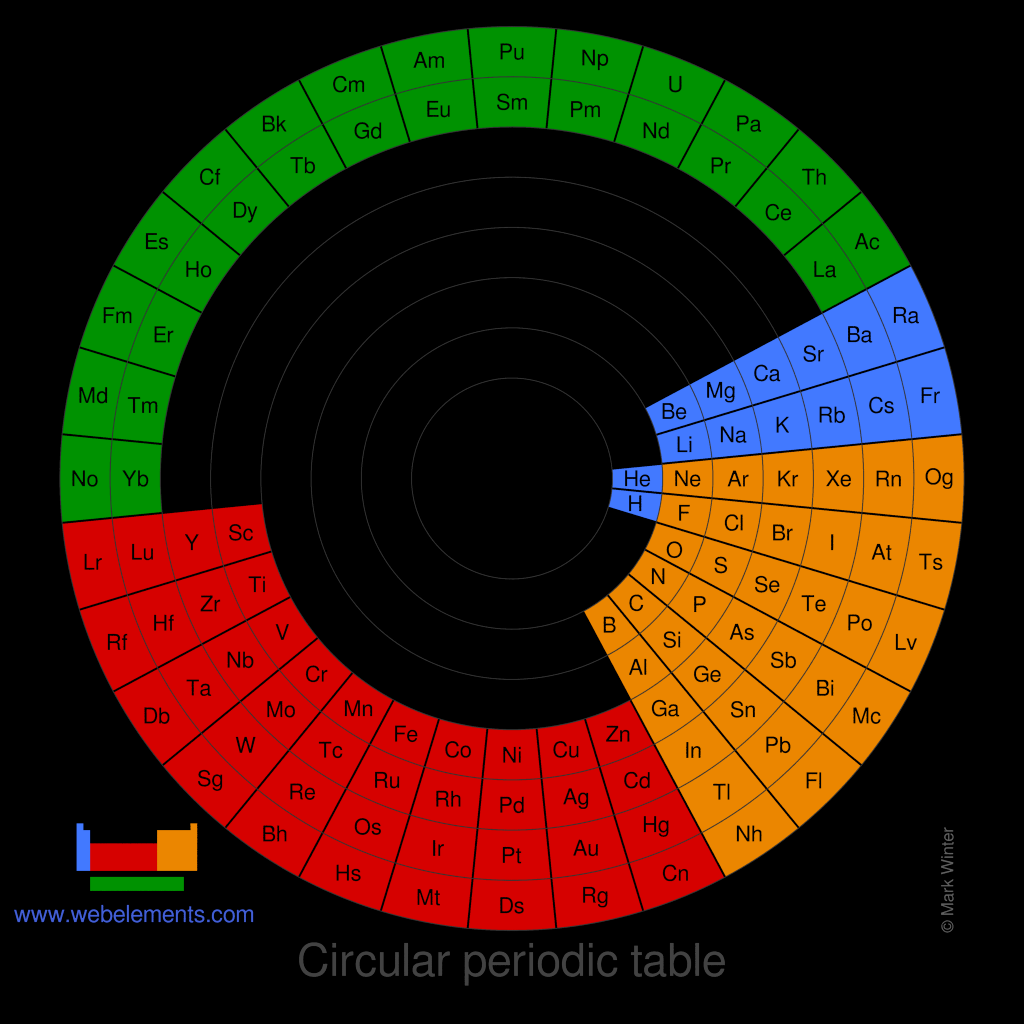
Image of an alternative circular periodic table of the elements
Images of various periodic tables
There are many variants of the periodic table, some useful, others less so. A few are linked shown below. Click on the images below to see images of the periodic table in a variety of styles. Many other periodic table formats are catalogued at Mark Leach's Meta-synthesis web site. A classic book showing many forms of the periodic table in print is: Edward G. Mazurs, Periodic representations of the periodic system during one hundred years, University of Alabama Press USA, 2nd edition, 1974. ISBN: 0-8173-3200-6.
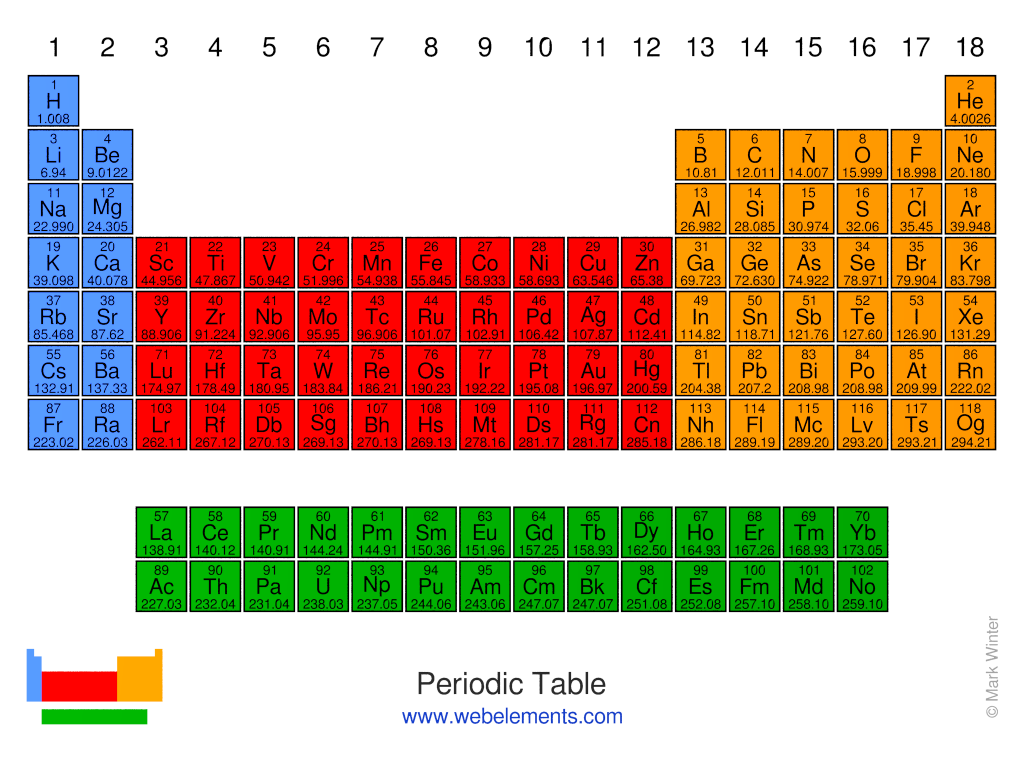
Explore the chemical elements through this (standard) periodic table
| Group | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period 1 |
1
1.008
Hydrogen
|
2
4.0026
Helium
|
|||||||||||||||||
| 2 |
3
6.94
Lithium
|
4
9.0122
Beryllium
|
5
10.81
Boron
|
6
12.011
Carbon
|
7
14.007
Nitrogen
|
8
15.999
Oxygen
|
9
18.998
Fluorine
|
10
20.180
Neon
|
|||||||||||
| 3 |
11
22.990
Sodium
|
12
24.305
Magnesium
|
13
26.982
Aluminium
|
14
28.085
Silicon
|
15
30.974
Phosphorus
|
16
32.06
Sulfur
|
17
35.45
Chlorine
|
18
39.948
Argon
|
|||||||||||
| 4 |
19
39.098
Potassium
|
20
40.078
Calcium
|
21
44.956
Scandium
|
22
47.867
Titanium
|
23
50.942
Vanadium
|
24
51.996
Chromium
|
25
54.938
Manganese
|
26
55.845
Iron
|
27
58.933
Cobalt
|
28
58.693
Nickel
|
29
63.546
Copper
|
30
65.38
Zinc
|
31
69.723
Gallium
|
32
72.630
Germanium
|
33
74.922
Arsenic
|
34
78.971
Selenium
|
35
79.904
Bromine
|
36
83.798
Krypton
|
|
| 5 |
37
85.468
Rubidium
|
38
87.62
Strontium
|
39
88.906
Yttrium
|
40
91.224
Zirconium
|
41
92.906
Niobium
|
42
95.95
Molybdenum
|
43
Tc ☢
96.906
Technetium
|
44
101.07
Ruthenium
|
45
102.91
Rhodium
|
46
106.42
Palladium
|
47
107.87
Silver
|
48
112.41
Cadmium
|
49
114.82
Indium
|
50
118.71
Tin
|
51
121.76
Antimony
|
52
127.60
Tellurium
|
53
126.90
Iodine
|
54
131.29
Xenon
|
|
| 6 |
55
132.91
Caesium
|
56
137.33
Barium
|
* |
71
174.97
Lutetium
|
72
178.49
Hafnium
|
73
180.95
Tantalum
|
74
183.84
Tungsten
|
75
186.21
Rhenium
|
76
190.23
Osmium
|
77
192.22
Iridium
|
78
195.08
Platinum
|
79
196.97
Gold
|
80
200.59
Mercury
|
81
204.38
Thallium
|
82
207.2
Lead
|
83
208.98
Bismuth
|
84
Po ☢
208.98
Polonium
|
85
At ☢
209.99
Astatine
|
86
Rn ☢
222.02
Radon
|
| 7 |
87
Fr ☢
223.02
Francium
|
88
Ra ☢
226.03
Radium
|
** |
103
Lr ☢
262.11
Lawrencium
|
104
Rf ☢
267.12
Rutherfordium
|
105
Db ☢
270.13
Dubnium
|
106
Sg ☢
269.13
Seaborgium
|
107
Bh ☢
270.13
Bohrium
|
108
Hs ☢
269.13
Hassium
|
109
Mt ☢
278.16
Meitnerium
|
110
Ds ☢
281.17
Darmstadtium
|
111
Rg ☢
281.17
Roentgenium
|
112
Cn ☢
285.18
Copernicium
|
113
Nh ☢
286.18
Nihonium
|
114
Fl ☢
289.19
Flerovium
|
115
Mc ☢
289.20
Moscovium
|
116
Lv ☢
293.20
Livermorium
|
117
Ts ☢
293.21
Tennessine
|
118
Og ☢
294.21
Oganesson
|
| *Lanthanoids | * |
57
138.91
Lanthanum
|
58
140.12
Cerium
|
59
140.91
Praseodymium
|
60
144.24
Neodymium
|
61
Pm ☢
144.91
Promethium
|
62
150.36
Samarium
|
63
151.96
Europium
|
64
157.25
Gadolinium
|
65
158.93
Terbium
|
66
162.50
Dysprosium
|
67
164.93
Holmium
|
68
167.26
Erbium
|
69
168.93
Thulium
|
70
173.05
Ytterbium
|
||||
| **Actinoids | ** |
89
Ac ☢
227.03
Actinium
|
90
Th ☢
232.04
Thorium
|
91
Pa ☢
231.04
Protactinium
|
92
U ☢
238.03
Uranium
|
93
Np ☢
237.05
Neptunium
|
94
Pu ☢
244.06
Plutonium
|
95
Am ☢
243.06
Americium
|
96
Cm ☢
247.07
Curium
|
97
Bk ☢
247.07
Berkelium
|
98
Cf ☢
251.08
Californium
|
99
Es ☢
252.08
Einsteinium
|
100
Fm ☢
257.10
Fermium
|
101
Md ☢
258.10
Mendelevium
|
102
No ☢
259.10
Nobelium
|
||||
The standard form of the periodic table shown here includes periods (shown horizontally) and groups (shown vertically). The properties of elements in groups are similar in some respects to each other.